WiTTY: Web-based interactive TTY
This program allows you to use terminal in the browser. Simply run the program and give it the command to execute when users connect via the browser. The main design goal of this tool is to help teaching courses that use Unix-like CLI environment. WiTTY has the following features that distinguish itself from other similar tools:
It allows others to view onging interactive sessions. This is useful for providing live remote support and/or help (only use this after user authentication is implemented).
A challenge of this use case is that our home networks are almost always behind NAT, making it diffcult to run WiTTY as a publicly accessible server. Security is also a concern. It is generally safer to use WiTTY in a trusted environment.
WiTTY allows users to easily record, replay, and share console sessions with just a few clicks. This make it a breeze to answer course-related questions, espeically with the source code. Instead of wall of text to describe their questions, students can just send a recorded session.
This repository contains a recorded session in the
assets/extradirectory (M1NXZvHdvA8vSCKp_61e5d60f.rec) that shows me upgrading pihole. Just put the file under therecordsdirectory, run the server, you should find the recording in theSaved Sessiontab.More features are planned, including user authentication. Suggestions are welcome.
You can use WiTTY to run any command line programs, such as
bash, htop, vi, ssh.
This following screenshot shows that three interactive session running
zsh on macOS Monterey.

The following screenshot shows three recorded sessions. You can
replay/download/delete them.

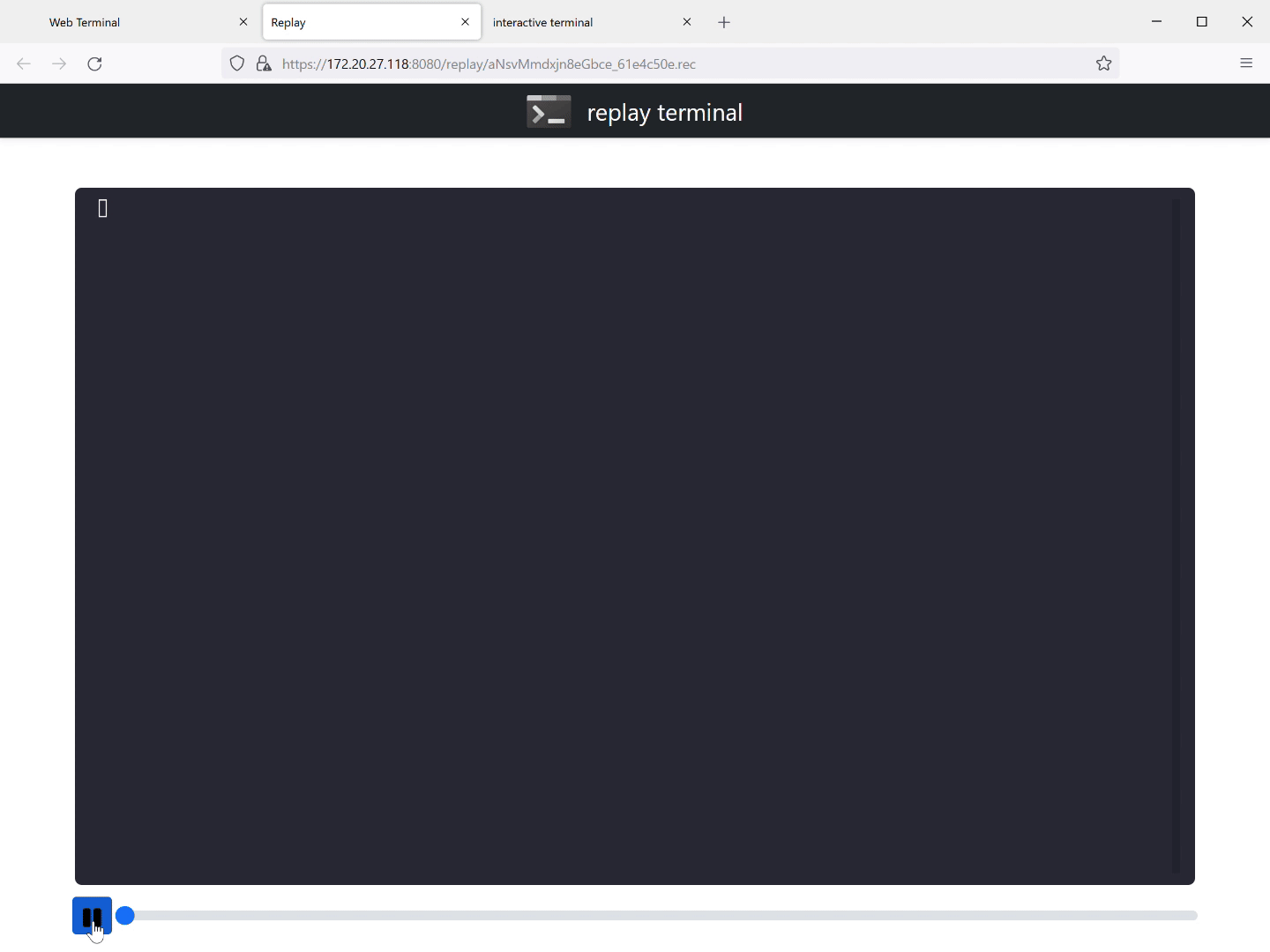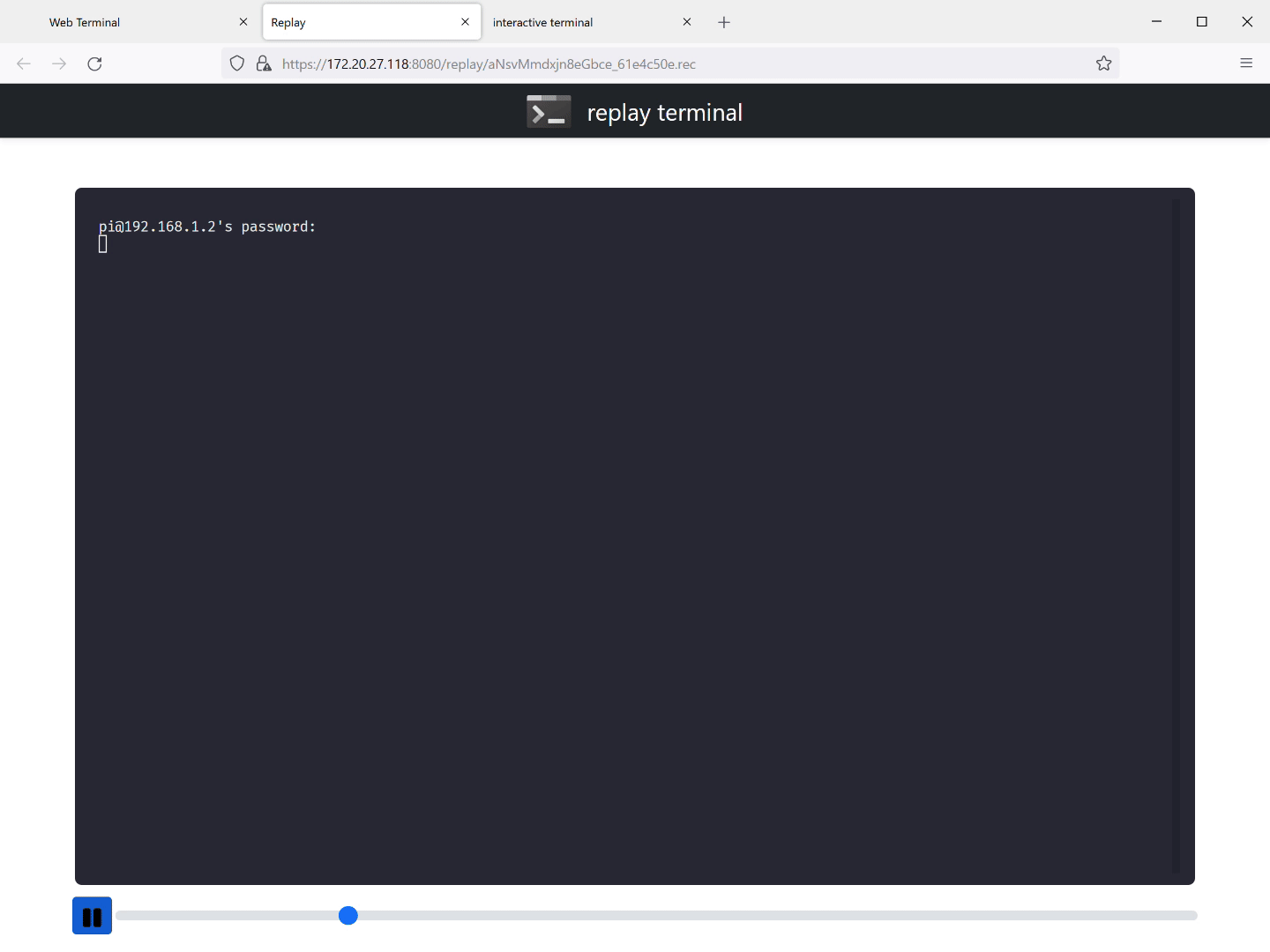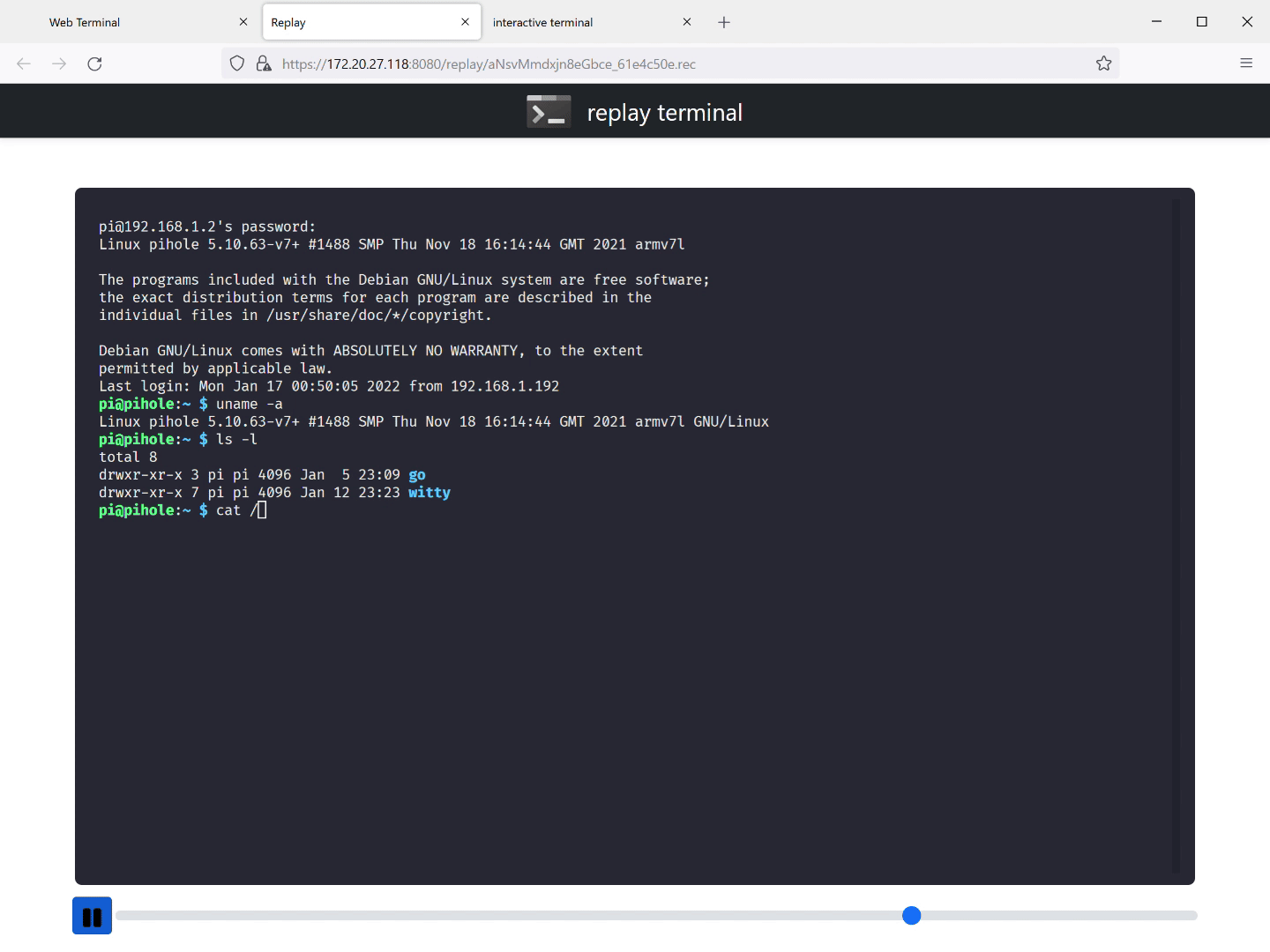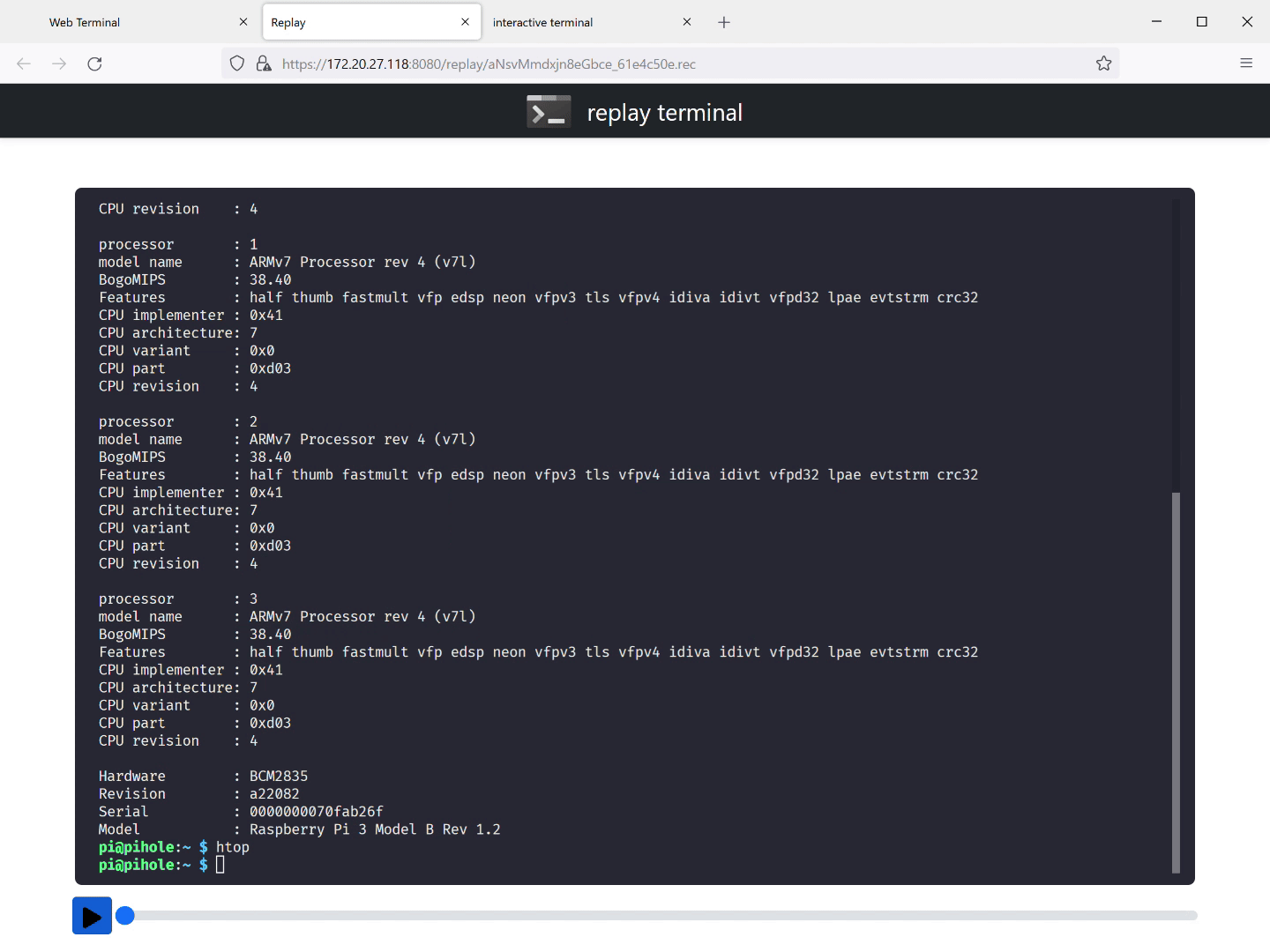
Here is a session, where we sshed into a Raspberry Pi running pi-hole
(./witty ssh 192.168.1.2 -l pi, WiTTY runs in a WSL2 VM on
Windows) being replayed. You can play/pause the session.
To use the program, you need to provide a TLS cert. You can request a
free Let’s Encrypt cert or use a
self-signed cert. The program currently does not support user
authentication. Therefore, do not run it in untrusted networks or leave
it running. A probably safe use of the program is to run
ssh. Please ensure that you do not automatically login to
the ssh server (e.g., via key authentication).
AGAIN, Do NOT run this in an untrusted network. You will expose your shell to anyone that can access your network and Do NOT leave the server running.
This program is written in the go
programming language, using the Gin web framework, gorilla/websocket, pty, and the wonderful xterm.js! The workflow is simple, the
client will initiate a terminal window (xterm.js) and create a websocket
with the server, which relays the data between pty and xterm. You can
customize the look and feel of the HTML pages by editing files under the
assets directory.
Installation
Install the go compiler. Make sure your have go 1.17 or higher.
Download the release and unzip it, or clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/syssecfsu/witty.gitGo to the
tlsdirectory and create a self-signed cert# Generate a private key for a curve
openssl ecparam -name prime256v1 -genkey -noout -out private-key.pem# Create a self-signed certificate
openssl req -new -x509 -key private-key.pem -out cert.pem -days 360Return to the root directory of the source code and build the program
go build .Start the server and give it the command to run. The server listens on 8080, for example:
./witty htopor./witty ssh <ssh_server_ip> -l <user_name>Connect to the server, for example
https://<witty_server_ip>:8080
The program has been tested on Linux, WSL2, Raspberry Pi 3B (Debian), and MacOSX using Google Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.